|
MAIN PAGE
> Back to contents
Psychologist
Reference:
Gvozdeva A.A., Zinatullina A.M.
The effectiveness of using virtual technologies to teach students life safety techniques
// Psychologist.
2023. ¹ 5.
P. 193-205.
DOI: 10.25136/2409-8701.2023.5.68725 EDN: FDQLWL URL: https://en.nbpublish.com/library_read_article.php?id=68725
The effectiveness of using virtual technologies to teach students life safety techniques
Gvozdeva Anastasiya Andreevna
Psychologist, Moscow State University of Psychology and Education, Faculty of Extreme Psychology
127051, Russia, Moscow region, Moscow, Sretenka str., 29

|
gvozdeva.anastasia2018@yandex.ru
|
|
 |
|
Zinatullina Azaliia Maratovna
Lecturer, Department of Scientific Basis of Extreme Psychology, Moscow State University of Psychology and Education
127051, Russia, Moscow region, Moscow, Sretenka str., 29

|
azaliazinatullina@mail.ru
|
|
 |
|
DOI: 10.25136/2409-8701.2023.5.68725
EDN: FDQLWL
Received:
16-10-2023
Published:
06-11-2023
Abstract:
Purpose of the study: theoretical and empirical study of the effectiveness of professional psychological preparation for activities in extreme conditions using virtual technologies. Object of study: professional and psychological preparation for activity. Subject of research: the use of VR technologies for professional and psychological preparation for activities in extreme conditions. The research was carried out using theoretical and empirical methods: experiment, testing, analysis and synthesis, comparison, generalization. Research methods: Questionnaire «Well-being, activity, mood». «Personal risk readiness». Measurement of heart rate. Achievement test. «First aid for electric shock». The situation was formed in extreme conditions, using the ARPort SafetyVR program in the «First Aid in the event of an electric shock» mode. Methods of mathematical statistics: Mean value, standard deviation, Mann-Whitney U-test, ANOVA. The sample consisted of 32 people, students studying in the field of «Extreme Psychology» at MSUPE. The results show that the use of virtual programs aimed at training and developing skills in dangerous situations is an effective way to form professional and psychological preparation of students for activities in extreme conditions and to optimize their indicators of well-being, mood and general activity. Studying the literature and the data obtained, we can say that modern virtual technologies can be successfully used in psychological work. These studies can be used to develop training using virtual reality technologies for representatives of high-risk professions or to prepare specialists for activities in extreme conditions
Keywords:
virtual programs, virtual technologies, VR-programs, extreme situations, psychological preparation, professional preparation, first aid, high-risk professions, electric shock, life safety
This article is automatically translated.
You can find original text of the article here.
Literature review Every year, technical development is gaining momentum more and more. There are new devices that improve people's lives. Technologies are also being created whose application contributes to the advancement of science. In particular, it can be noted how extensively virtual technologies are used in various spheres of life. The use of simulation of the "other" world could not fail to interest psychologists who study the human psyche, its interaction with the outside world and itself [1;2]. The possibility of creating completely different conditions has opened up many opportunities for studying the reactions that arise in humans [3; 4]. In particular, virtual technologies are actively used to study human reactions to extreme environments. After all, the creation of real extreme situations contributes to the high risk of training employees who do not yet have sufficient experience. Therefore, it is necessary to recreate similar conditions, but without risk to life and health. Virtual technologies help to accomplish this task. Thus, they are used to acquire the necessary knowledge about the hazardous environment, its geographical location, the likely forms of danger (fire, electric shock, etc.) [5]. Knowledge, backed up by a virtual picture, sounds, and ways of virtual interaction of an employee with the presented environment, helps to gradually develop the skills necessary for adaptation. The availability of programs dedicated to various types of professional activities, various extreme situations that require a quick and clear solution, makes it possible to prepare almost every employee in accordance with his specialty [6; 7; 8]. I would like to pay special attention to the work of specialists in the field of high electrical voltage. There is a need to develop not only theoretical, but practical skills in working with current. However, preparation for this activity is complicated due to the risk of an electric shock by a specialist. Creating learning situations that mimic real activity does not always convey its features, as well as its danger. This requires new training options, for example, immersion in virtual reality[1]. With the help of virtual technologies, it is possible to work out a wide variety of situations from the simplest to extreme, and in controlled, safe conditions. After all, an inexperienced specialist may experience fear, self-doubt, and in case of an emergency, he may not decide to take active action. And procrastination, incorrect actions in emergency moments can lead to serious losses and even deaths of people [9]. Special training with the help of virtual technologies allows you to consolidate existing theoretical knowledge and begin to actualize practical ones, which together will make up those initial skills that allow the employee to gradually move on to more complex and real cases. Moreover, such training will allow you to prepare a specialist both in the field of professional skills and in the field of psychological. As part of this, the project "Virtual Electrician" is interesting, implemented in the branch of JSC "Grid Company" Nizhnekamsk Electric Networks, which is carried out through the use of virtual technologies [10]. With the help of virtual glasses, the student watches a video, which clearly reflects the stages of actions during the performance of certain works, indicates possible dangers that may arise in the process. Such training contributes to faster training of electricians, especially in combination in the work of a novice specialist with a more experienced one. The program reflects a large number of important details that are characteristic of certain situations and operations performed that correspond to real ones. The use of the simulator contributes to a stronger consolidation of knowledge and practical skills, besides, this format is more interesting for employees to pass. Repeated development of a professional algorithm of actions with the help of a simulator will allow to achieve the necessary professional and psychological training of an electrician. The application of new technologies is also carried out in the field of fire extinguishing training. The study "The Evaluation of Virtual Reality Fire Extinguisher Training" conducted in 2020 in Norway [11] was aimed at finding out how trainees evaluate their training in handling a fire extinguisher in virtual reality. The results showed that more than half of the listeners positively assessed the VR training and reported positive emotions during the workout. However, most preferred traditional training or treated it neutrally. The two main topics that the participants evaluated differently were the realism of learning and their emotional experiences during a virtual reality session. While virtual reality training at this stage was seen as a good complement to real learning, its lack of realism was a serious disadvantage, but the health and safety benefits, as well as the efficiency and convenience of this training were obvious advantages over real learning. In the study "Understanding VR—Based Construction Safety Training Effectiveness: The Role of Telepresence, Risk Perception, and Training Satisfaction", conducted in Korea in 2022 [12], analyzed data from a survey of 248 builders who were trained in safety during construction using virtual reality. According to the results obtained, it was noted that the use of virtual technologies, their visibility and interactivity had a great impact on the results of training security techniques. It is also important to note that the builders themselves noted satisfaction after the past classes, they themselves felt the positive effect of the impact. Due to the abundance of research [13;14], the relevance of professional and psychological training of specialists for the effective implementation of work activities in extreme activities is revealed. And the relevance of the topic is the reason for this study. Organization of research The purpose of the study is to study the effectiveness of the use of virtual technologies for the implementation of professional and psychological preparation of students for activities in extreme conditions.
The object of research: professional and psychological preparation for activity. Subject of research: the use of VR technologies for professional and psychological preparation for activities in extreme conditions. The research was carried out using theoretical and empirical methods: experiment, testing, analysis and synthesis, comparison, generalization. The hypothesis is the assumption that the use of virtual technologies aimed at developing skills in dangerous situations contributes to improving the professional and psychological preparation of employees for activities in extreme conditions and optimizing their indicators of well—being, mood and general activity. Research methods: 1. Questionnaire "Well-being, activity, mood" (SAN). Authors: V. A. Doskin, N. A. Lavrentieva, V. B. Sharai, M. P. Miroshnikov, Karelin A. 2. Personal risk-taking. Author: A.M. Shubert. 3. Measurement of the psychophysiological component of the functional state. Measurement of heart rate (heart rate). 4. Achievement test. "First aid in case of electric shock". Author's development. An extreme situation was also simulated using virtual reality technologies. With the help of the ARPort SafetyVR program in the "First aid in case of electric shock" mode, the subjects were offered to undergo training in working under high voltage conditions, as well as to fulfill the goal and save the victim who is under the influence of electric current, and at the same time not to get into mortal danger himself. The extreme impact was within 10 minutes. During the training, the subjects learned to pay attention to the situation, assess possible risks, build an algorithm of behavior that allowed to eliminate or avoid the detected danger, as well as spend the optimal amount of time on it. The participants paid more attention to the current situation, where there is a high probability of receiving an electric shock. They got acquainted with the peculiarities of the propagation and conduction of current through space and materials, learned about the correct algorithm of actions when in the field of step voltage. Took part in the evacuation of the victim. They learned how to de-energize a person, how correctly it can be taken after that, for which parts of the body, how far it is necessary to drag a person away from the electric shock zone, what biological processes need to be checked, how to provide first aid, etc. At the beginning of the training program, the purpose of the lesson is announced, and in its process it is noted which step needs to be performed at the moment and what you should pay attention to in order to successfully complete it. Mistakes entail the loss of points, and fatal mistakes, therefore, the death of the rescuer. Moreover, it is accompanied by a sudden and strong vibration in the joysticks (imitation of an electric shock), as well as a display of how the rescuer controlled by the player falls to the ground. Then it was announced what was the result of such an outcome, in which a mistake was made. For some subjects, the combination of the above elements caused fright. After each fatal mistake, the participants started training again from the very beginning. Through the acquisition of theoretical and practical knowledge, they successfully learned how to provide first aid to an electric shock victim. Equipment used: Vive Focus Plus. Methods of mathematical statistics: Mean value, standard deviation, Mann—Whitney U—Test, ANOVA. The sample consisted of 32 people, students studying in the direction of "Extreme Psychology" at MGPPU. Research results and their analysis Initially, tests and measurements were carried out (SAN, risk readiness, Achievement Test. "First aid in case of electric shock", heart rate) in 32 students from the department of "Extreme Psychology". Diagnostics of the level of activity training in the high voltage zone was carried out. After that, according to the results, 20 people were selected. 10 of them were included in the experimental group, and 10 others were included in the control group. The experimental group took part in the training program using virtual technologies. The control group was not exposed to any effects. Upon successful completion of professional and psychological training, information on testing was collected from the experimental group again. The control group was also tested for the second time. A study of well-being, mood, activity, risk readiness level, the results of first aid testing as a result of an electric shock, as well as pulse measurement of all 32 subjects were conducted before the groups were isolated and experimental exposure was carried out. The analysis yielded the following results. Table 1 — Indicators of the entire sample before the selection of groups and experimental exposure | ¹ |
Indicator | Arithmetic mean | Standard deviation | | 1 | Achievement Test | 5,44 | 1,585 | | 2 | Well-being | 44,94 | 13,629 | | 3 | Activity | 39,78 | 11,653 | | 4 | Mood | 47,84 |
12,741 | | 5 | Risk | -1,69 | 13,642 | | 6 | Pulse | 77,00 | 10,192 | According to Table 1, it can be understood that "Testing" (Test of achievements. "First aid in case of electric shock"), passed by 32 subjects on average was rated at 5 out of 10 points, which shows the average level of knowledge on first aid in case of electric shock. The average state of health in the sample scored 44.94 points, which indicates a favorable condition of the subjects. Activity averaged 39.78 points, these indicators reflect slightly lowered values for activity. The average mood scored 47.84 points, which also reflects the favorable mood of the subjects. Risk readiness is shown on average at the level of -1.69, which indicates the average values of risk propensity among the respondents. The pulse on average is 77 beats per minute, which reflects the indicators within the norm. At the next stage, 20 people with the lowest values on the Achievement Test were selected from 32 people. "First aid in case of electric shock to participate in the experiment." These 20 people were divided into 2 groups: the experimental group (EP) and the control group (KG). In order to find out if there are differences in the indicators of KG and EG, a nonparametric U—Mann—Whitney criterion was applied at the first measurement. Table 2 — Comparison of KG and EG indicators at the first measurement, before exposure | ¹ | Indicator | Criterion U | P= |
| 1 | Achievement Test | 0,78 | p?o,o5 | | 2 | Well-being | 0,21 | p?o,o5 | | 3 | Activity | 0,705 | p?o,o5 | | 4 | Mood | 0,088 | p?o,o5 | | 5 | Risk |
0,058 | p?o,o5 | | 6 | Pulse | 0,733 | p?o,o5 | In Table 2, it can be seen that there are no significant differences in the indicators of KG and EG. This means that the groups do not significantly differ in the results of the methods. But it is possible to distinguish the results on "Mood" and "risk readiness", the significance of which is manifested at the level of trends U=27.5 and U=25 at p? 0.05. At the next stage, a stressful effect was exerted through VR glasses. The EG was experimentally affected, but the KG was not. To determine the presence of any changes, one-factor analysis of variance ANOVA was applied. Table 3 — Comparison of indicators 1 and 2 measurements in KG | ¹ | Indicator | 1 measurement of average values | 2 measurement of average values | 1 measurement standard deviation | 2 measurement standard deviation | Criterion F | P= | | 1 | Achievement Test |
4,7 | 5 | 0,94868 | 1,24722 | 0,552 | p?o,o5 | | 2 | Well-being | 38,9 | 39,2 | 14,84326 | 15,12761 | 0,965 | p?o,o5 | | 3 | Activity | 37 | 39,8 | 13,41641 |
13,11318 | 0,643 | p?o,o5 | | 4 | Mood | 41,6 | 43,7 | 13,4594 | 17,23723 | 0,765 | p?o,o5 | | 5 | Risk | -0,3 | -1,2 | 15,74131 | 13,33167 | 0,892 | p?o,o5 | | 6 |
Pulse | 77,9 | 78,7 | 12,96534 | 10,53091 | 0,881 | p?o,o5 | As can be seen from table 3, there are no significant results. The indicators when passing the techniques for the first and second time do not significantly differ. The results of the Achievement Test. "First aid in case of electric shock", SAN, risk preparedness, heart rate have no significant differences between the first and second measurements. Table 4 — Comparison of indicators 1 and 2 measurements, before and after experimental exposure in EC | ¹ | Indicator | 1 measurement of average values | 2 measurement of average values | 1 measurement standard deviation | 2 measurement standard deviation | Criterion F | P= | | 1 | Achievement Test |
4,4 | 7,3 | 1,26491 | 1,1595 | 0,0 | p?o,oo1 | | 2 | Well-being | 48 | 54,8 | 15,4991 | 12,891 | 0,3 | p?o,o5 | | 3 | Activity | 40,1 | 49,8 | 13,77961 | 10,37947 |
0,092 | p?o,o5 | | 4 | Mood | 52 | 53,6 | 14 | 12,50955 | 0,791 | p?o,o5 | | 5 | Risk | -10,2 | -7,6 | 11,35097 | 10,38375 | 0,6 | p?o,o5 | | 6 |
Pulse | 75,7 | 79,5 | 8,70568 | 14,13624 | 0,478 | p?o,o5 | Graph 1 — Indicator "Test" - the result of passing the Achievement Test. "First aid in case of electric shock to the EG before and after experimental exposure Graph 2 — The indicator "Activity" is the result of EG on a scale from the SAN methodology before and after experimental exposure 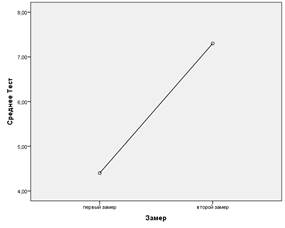 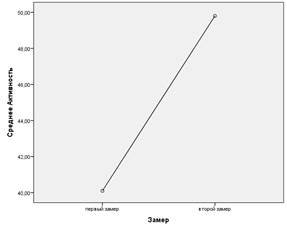
Calculations based on the ANOVA one-factor analysis of variance showed significant results in the indicators of the Achievement Test in Table 4. "First aid in case of electric shock" at the level of high significance F=28.562 at p?0.001. Also interesting are the indicators for "Activity" from the SAN methodology, which show significance at the level of trends F= 3.162 at p ? 0.05. The indicators of the experimental group of subjects for all methods after passing the training program significantly increased, which can be seen in Table 4, as well as graphs 1-2. Testing results have improved. The indicators for "Mood" have only slightly increased, although they were initially high, they have remained the same high. "Well-being" has improved to high levels, which reflects positive changes in students' self-perception. Also, the indicators for "Activity" almost reached high values. It is important to note that the heart rate indicators are within the norm, including the level of risk. This indicates the effectiveness of the extreme exposure and the successful implementation of professional and psychological training, which is expressed in optimal values for risk readiness, pulse, well—being, activity, mood. Discussion of the results The indicators of the experimental group of subjects for all methods after passing the training program significantly increased, which can be seen in the table, as well as graphs No. 1-2. The results of the "First aid in case of electric shock" testing have improved. The indicators for "Mood" have only slightly increased, although they were initially high, they have remained the same. "Well-being" has improved to high levels, which reflects positive changes in students' self-perception. Also, the indicators for "Activity" almost reached high values. It is important to note that the heart rate indicators are within the norm, including the level of risk. This indicates the effectiveness of the extreme exposure and the successful implementation of professional and psychological training, which is expressed in optimal values for risk readiness, pulse, well-being, activity, mood. To compare the indicators of KG, which was not experimentally affected. A study of the indicators of the control group at the first and second measurements was carried out. Summing up the analyzed data, we can say the following: The results for the entire sample of 32 people are within the norm. The indicators of the control group in the second measurement in comparison with the first do not differ significantly. There are no significant results.
The results of the experimental group significantly differ in the indicators of the "Test" (Test of achievements. "First aid in case of electric shock") and have a high level of significance at p?0.001. Which indicates the great influence that was exerted on the experimental group with the help of the training program. The indicator "Activity" at the level of trends is also highlighted. Comparing the average values for KG and the average values for EG for each measurement, you can see a big difference, which manifests itself in a significant increase in indicators at the second measurement in comparison with the first. This is observed in an experimental group that underwent a training program. And the control group, which was not exposed to any effects, has no significant changes. Conclusion Analyzing the results, we can say that the impact on the experimental group was effective, which confirms the hypothesis that the use of virtual technologies aimed at developing skills in dangerous situations contributes to improving the professional and psychological preparation of students for activities in extreme conditions and optimizing their indicators of well—being, mood and general activity. Studying the literature and the data obtained, we can say that modern virtual technologies can be successfully used in psychological work. The accelerated pace of development of such technologies presupposes a psychological view that keeps pace with them, which promotes the use of such technologies in the work of a psychologist. For the development and improvement of work with virtual technologies, additional theoretical and practical research is required on the effectiveness of psychological influence in various fields and goals of psychological work. In addition, it is important to inform the scientific community about the scientifically proven results and introduce new methods into their work and develop their applications within psychology. These studies can be used as a basis for the development of special trainings using virtual reality technologies for representatives of high-risk professions or for training specialists to work in extreme conditions. Acknowledgements: I would like to express special gratitude to T. N. Berezina, K.E. Buzanov and ARPort LLC. [1] ARPort. VR simulators for occupational safety and PTM. URL: https://www.arport.ru/vr-safety (date of application:31.07.2023).
References
1. Berezina, T.N., Perepechina, A.S., & Buzanov, K.E. (2020). Correction of negative mental states of extreme profile psychology students using virtual reality technologies. Modern education, 4, 1-12.
2. Berezina, T.N., Temirkanova, A.Yu., Bortuleva, N.L., Svilo, Ya.V. (2020) Restoring working capacity through VR technologies for people combining work with study. Modern education, 3, 11-20.
3. Berezina, T. N. (2020). Positive psychology of virtuality as a direction for optimizing the functional states of a human operator. T. N. Berezina, K. E. Buzanov, G. V. Fatyanov (Eds.). Human capital, 1(133), 125-138.
4. Litvinova A.V., Berezina T.N., Kokurin A.V., & Ekimova V.I. (2022). Psychological safety of students in interaction with virtual reality. Modern foreign psychology, 11(3), 94-104.
5. Vyaltsev, A.V., Pavlov, M.M., Yants, A.I. (2017) The use of virtual reality technologies in the training of mine rescuers. Innovative science, 1–2, 59–61.
6. Badzyuk, I.L., & Chepurnykh, N.K. (2021). Application of virtual reality technology in teaching first aid skills: scientific basis, practical experience. Education and Law, 9, 279-286.
7. Tumakov, N. N. (2020). The use of computer simulators in training military personnel in tactical and special disciplines in the airborne school. Current problems of teaching mathematical and natural science disciplines in educational institutions of higher education: Materials of the All-Russian scientific and methodological conference, 428-434.
8. Tychkov, A. Yu., Bunygin, E. V. (2020). Virtual reality for the armed forces: a review. Bulletin of Penza State University, 32(4), 107-114.
9. Rosenova, M.I. (2020). Stress and fear in extreme situations. M.I. Rosenova, V.I. Ekimova, A.V. Kokurin, A.S. Ognev, O.S. Efimova. Modern foreign psychology, 9(1), 94–102.
10. How to prepare an electrician: Project “Virtual Electrician”. Retrieved from https://up-pro.ru/library/personnel_management/personnel_training/kak-podgotovit-elektromontera/
11. Saghafian, M, Laumann, K, Akhtar, R.S., & Skogstad, M.R. (2020). The Evaluation of Virtual Reality Fire Extinguisher Training. Front Psychol, 11. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7680855
12. Yoo J.W., Park J.S., & Park H.J. (2023). Understanding VR-Based Construction Safety Training Effectiveness: The Role of Telepresence, Risk Perception, and Training Satisfaction. Applied Sciences, 2, 13. Retrieved from https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3417/13/2/1135
13. Said N.B., Molassiotis A., Chiang V.C.L. (2022). Psychological first aid training in disaster preparedness for nurses working with emergencies and traumas. International Council of Nurses, 69(4), 548-558.
14. Sun Xin-Yang. (2014). Mental Health of Chinese Peacekeepers in Liberia. The European Journal of Psychiatry, 28(2), 77-85.
First Peer Review
Peer reviewers' evaluations remain confidential and are not disclosed to the public. Only external reviews, authorized for publication by the article's author(s), are made public. Typically, these final reviews are conducted after the manuscript's revision. Adhering to our double-blind review policy, the reviewer's identity is kept confidential.
The list of publisher reviewers can be found here.
All methods and means that are designed to ensure the safety of professional activity should be used only if they are useful and effective. Moreover, the effectiveness should be reliable. Otherwise, such methods and means have a negative impact on the activity and are accompanied by an increase in the number of danger risks. Where human security is concerned, there can be no middle ground. It is impossible to "clutter up" the workspace with means with unproven effectiveness in any case. Therefore, the author did the right thing by defining the effectiveness of the use of virtual technologies for teaching students life safety techniques as the topic of his research. But the name sounds more correct - evaluation of the effectiveness of the application… The text begins with the fact that "Technical development is gaining momentum every year." This is wrong. It is necessary to start by substantiating the relevance of the topic, adhering to the clarity of the presentation of existing problems, contradictions, misunderstandings, etc. The author begins to write about "turns" using a primitive household syllable. Therefore, it is advisable to rework the introduction of the article, indicating in it, in addition to substantiating relevance, scientific novelty and research methodology (principles, theories, concepts). The formulations of the purpose and subject of the study given in the text need to be adjusted. For example, the goal is not to study, but to research… The subject is not the application of VR technologies... but the method of application.... The author correctly focuses on the safety of the work of specialists in the field of high electrical voltage. And also on the fact that preparation for the performance of this activity is complicated due to the risk of an electric shock by a specialist. Creating learning situations that mimic real-world activities does not always convey its features, as well as its dangers. This requires new learning options, such as virtual reality immersion. All this is correct and there is no doubt about it. Moreover, as indicated in the text, with the help of virtual technologies, it is possible to work out a wide variety of situations from the simplest to the most extreme, and in controlled, safe conditions. The style of presentation of the text is exploratory. The author analyzes the literature, makes his own conclusions. He independently organized the research, selected methods, conducted an experiment and received his own data. The structure of the work meets the requirements in general. Further work is needed on the above comments, and it is also necessary to present specific conclusions. The essence of the experiment is that with the help of a special simulator, an extreme situation was simulated using virtual reality technologies. With the help of the ARPort SafetyVR program in the "First aid in case of electric shock" mode, the subjects were offered to undergo training in working under high voltage conditions, as well as fulfill their goal and save the victim who is under the influence of electric current, and at the same time not get into mortal danger himself. The extreme impact was within 10 minutes. As a result of the study, the author found that the indicators of the experimental group of subjects according to all methods significantly increased after completing the training program. The indicators for "Mood" have only slightly increased, although they were initially high, they have remained the same high. "Well-being" has improved to high levels, reflecting positive changes in students' self-perception. Also, the indicators for "Activity" almost reached high values. It is important to note that heart rate indicators are within the norm, including the level of risk. The text also notes that the results of the experimental group differ significantly in the indicators of the "Test" (Test of achievements. "First aid in case of electric shock") and have a high level of significance at p?0.001. Which indicates the great influence that was exerted on the experimental group with the help of the training program. The author compared the indicators of the control and experimental groups. This allowed him to see a big difference, which manifests itself in a significant increase in performance at the second measurement compared to the first. This is observed in the experimental group that underwent the training program. And the control group, which was not exposed to any effects, has no significant changes. The data obtained are presented in the form of tables and figures, the contents of which are clear. The text contains a conclusion that reflects the essence of the work done. But there are no conclusions, which requires appropriate refinement. Moreover, there are enough facts for conclusions in this text. The bibliographic list consists of sources on the research topic. After finalizing the text, this article can be recommended for publication in a scientific journal.
Second Peer Review
Peer reviewers' evaluations remain confidential and are not disclosed to the public. Only external reviews, authorized for publication by the article's author(s), are made public. Typically, these final reviews are conducted after the manuscript's revision. Adhering to our double-blind review policy, the reviewer's identity is kept confidential.
The list of publisher reviewers can be found here.
The paper "The effectiveness of the use of virtual technologies for teaching students life safety techniques. The subject of the study. The work is aimed at studying the features of the use of VR technologies for professional and psychological preparation for activities in extreme conditions. The author suggested that the use of virtual technologies aimed at developing skills in dangerous situations contributes to improving the professional and psychological training of employees for activities in extreme conditions and optimizing their indicators of well—being, mood and general activity. In general, the conducted research is characterized by integrity, the set goals and objectives have been implemented. The research methodology is determined by the highlighted relevance. It was carried out using theoretical and empirical methods: experiment, testing, analysis and synthesis, comparison, generalization. The author carried out the simulation of an extreme situation using virtual reality technologies. The relevance of the research is determined by the fact that it is necessary to find effective technologies for teaching students life safety techniques and professional psychological preparation for activities in extreme conditions. The scientific novelty of the research. The conducted research allowed us to show the effectiveness of using VR technologies for professional and psychological preparation for activities in extreme conditions. The author clarified the categorical apparatus, selected research methods, developed and tested a training program. Style, structure, content. The style of presentation corresponds to publications of this level. The language of the work is scientific. The structure of the work is clearly traced, the author highlights the main semantic parts. The work begins with a literature review. In this section, attention is paid to the description of relevance both from the perspective of the relevance of studying virtual technologies, and in terms of the need for more effective training of relevant specialists to work in extreme activities. The next section is devoted to the description of the organization of the study. The author identified its purpose, object, and subject; formulated a hypothesis and selected research methods and techniques (empirical and mathematical statistics methods). The sample consisted of 32 students who study in the direction of "Extreme Psychology" at MGPPU. The next section is devoted to the description of the research results, their analysis and discussion. The results obtained were examined using mathematical statistics methods. The author presented the data in the form of tables and graphs. In conclusion, the final summary conclusions are formulated. The author notes the following: - the proposed hypothesis has been empirically confirmed; - modern virtual technologies can be successfully used in psychological work. Bibliography. The bibliography of the article includes 14 domestic and foreign sources, a significant part of which has been published in the last three years. The list contains mainly articles and abstracts. In addition, there are Internet sources in the bibliography. The sources are mostly designed correctly and uniformly. With the exception of paragraph 7. Appeal to opponents. Recommendations: - highlight the introduction in a separate section; - SAN questionnaire, achievement test, etc. are methods; - expand the section "Discussion of results" by presenting a more complete analysis of the results obtained; - to describe in more detail the content of the training program, the principles of its formation and application; - to present the main directions of training work using virtual reality technologies for representatives of high-risk professions or for training specialists for activities in extreme conditions. Conclusions. The problems of the article are of undoubted relevance, theoretical and practical value; it will be of interest to specialists who deal with the issues of training specialists working in extreme conditions. The article can be recommended for publication taking into account the highlighted recommendations.
Link to this article
You can simply select and copy link from below text field.
|
|




